The design of the vessels was defined on drawings that nominated a minimum number of 500 000 cycles over a 0 to 280 kPa pressure range. Vessel loading data was collected and provided which was considered representative of the vessel service.
Scope Of Work
Fatigue damage in the vessel using a damage tolerance approach to estimate remaining life by applying the principles of API 579-1 / ASME FFS-1 Fitness for Service (Level 1 / Level 2):
- Quantify loading data.
- Elastic stress analysis (equivalent structural stress).
- Identify critical locations and assess fatigue damage.
- Estimate remaining life based on historical loading data.
Project Challenges
- The assessment assumed the only significant stress cycling is due to pressure fluctuations and not been operated under process conditions that induce material embrittlement.
- The critical areas from the total stress distribution were linearized, on a stress component basis, to categorize the stresses into various stress categories.
How We Managed This
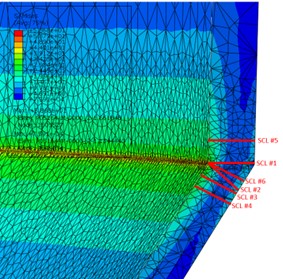
- The stress linearization feature in the Abaqus FEA software was used to separate the total stress distribution into membrane, bending, and peak stresses.
- The stress linearization feature required a stress classification line (SCL) to be drawn through a cross-section of the model or otherwise known as the stress classification plane (SCP).
Value Engineering
The owner was considering costly vessel replacements, but a computer-assisted appraisal enabled a confident quantification of the remaining vessel life, proving to be a much more economical solution.